Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Nakabayashi, Masakazu*; Oyama, Hidenori*; Hanano, N.*; Hirao, Toshio; Simoen, E.*; Claeys, C.*
Proceedings of the 6th International Workshop on Radiation Effects on Semiconductor Devices for Space Application (RASEDA-6), p.183 - 186, 2004/10
no abstracts in English
Chakoumakos, B. C.*; Rawn, C. J.*; Rondinone, A. J.*; Marshall, S. L.*; Stern, L. A.*; Circone, S.*; Kirby, S. H.*; Jones, C. Y.*; Toby, B. H.*; Ishii, Yoshinobu
Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Gas Hydrates (ICGH-4), p.655 - 658, 2002/05
no abstracts in English
Rawn, C. J.*; Rondinone, A. J.*; Chakoumakos, B. C.*; Marshall, S. L.*; Stern, L. A.*; Circone, S.*; Kirby, S. H.*; Jones, C. Y.*; Toby, B. H.*; Ishii, Yoshinobu
Proceedings of 4th International Conference on Gas Hydrates (ICGH-4), p.595 - 598, 2002/05
no abstracts in English
JNC TN8400 2001-008, 36 Pages, 2001/03
Research on geologic disposal of high-level radioactive waste(HLW) has been underway in many countries. Bentonite exhibiting a low permeability, high swelling property and high sorption capacity for many radioelements is proposed as a buffer material in many countlies. Recently, cementitious materials are considered as candidate matelials for the geologic disposal of high-level radioactive waste. As the pH and the Ca, Na, K contents of hyperalkaline pore water from the cementitious materials are high, this hyperalkaline pore water would alter the buffer material. The main aim of this study is to investigate the effect of alkaline pore water into the bentonite. Used materials are montmorillonite, albite and quartz composing bentonite. These minerals mixed in a constant ratio (1:1wt%) made to react to distilled water and the alkali solutions (pH11-13). These studies have been conducted at temperatures of 50 - 150 C and run times of 10 - 200 day. XRD(X-ray powder diffraction) and SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) analyses were applied to studying the structure and quantitative data of each sample. From the result of this study, the main formed mineral of this experiment was analcime, which showed the tendency with a large amount of generation at a higher pH and temperature. Quantitative data of this study was conducted by X-ray powder diffraction method. THe order of the amount of the second analcime in each experiment is shown in the following. Montmorillonite and albite mixing test
C and run times of 10 - 200 day. XRD(X-ray powder diffraction) and SEM (Scanning Electron Microscopy) analyses were applied to studying the structure and quantitative data of each sample. From the result of this study, the main formed mineral of this experiment was analcime, which showed the tendency with a large amount of generation at a higher pH and temperature. Quantitative data of this study was conducted by X-ray powder diffraction method. THe order of the amount of the second analcime in each experiment is shown in the following. Montmorillonite and albite mixing test  Montmorillonite test
Montmorillonite test  Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test Activation energies (E
Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test Activation energies (E ) using the quantitative data of each test are shown in the following. (1)Montmorillonite test : 54.9kJ/mol (2)Montmorillonite and albite mixing test : 51.9kJ/mol (3)Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test : 59.6kJ/mol
) using the quantitative data of each test are shown in the following. (1)Montmorillonite test : 54.9kJ/mol (2)Montmorillonite and albite mixing test : 51.9kJ/mol (3)Montmorillonite and quartz mixing test : 59.6kJ/mol
 to obtain the high U solution
to obtain the high U solution; *; Sakurai, Koji*; ; Nomura, Kazunori; *
JNC TN8400 2000-032, 98 Pages, 2000/12
Concerning the preparation of high U solution for the crystallization process and the application of UO powder dissolution to that, the effects of final U concentration, dissolution temperature, nitric acid concentration and powder size on the dissolution of UO
powder dissolution to that, the effects of final U concentration, dissolution temperature, nitric acid concentration and powder size on the dissolution of UO powder in the nitric acid where the final U concentration was
powder in the nitric acid where the final U concentration was  800g/L were investigated. The experimental results showed that the solubility of UO
800g/L were investigated. The experimental results showed that the solubility of UO decreased with the increase of final UO
decreased with the increase of final UO concentration and powder size, and with the decrease of dissolution temperature and nitric acid concentration. It was also confirmed that in the condition where the final U concentration was sufficiently lower than the solubility of U, UO
concentration and powder size, and with the decrease of dissolution temperature and nitric acid concentration. It was also confirmed that in the condition where the final U concentration was sufficiently lower than the solubility of U, UO dissolution behavior in the high U solution could be estimated with the equation based on the fragmentation model which we had already reported. Based on these experimental results, the dissolution behavior of irradiated MOX fuel in high U solution was estimated and the possibility of supplying high U solution to the crystallization process was discussed. In the preparation of high U solution for the crystallization process, it was estimated that the present dissolution process (dissolution for fuel pieces of about 3cm long) needed a lot of time to obtain a high dissolution yield, but it was shorted drastically by the pulverization of fuel pieces. The burst of off-gas at the early in the dissolution of fuel powder seems to be avoidable with setting the appropriate dissolution condition, and it is important to optimize the dissolution condition with considering the capacity of off-gas treatment process.
dissolution behavior in the high U solution could be estimated with the equation based on the fragmentation model which we had already reported. Based on these experimental results, the dissolution behavior of irradiated MOX fuel in high U solution was estimated and the possibility of supplying high U solution to the crystallization process was discussed. In the preparation of high U solution for the crystallization process, it was estimated that the present dissolution process (dissolution for fuel pieces of about 3cm long) needed a lot of time to obtain a high dissolution yield, but it was shorted drastically by the pulverization of fuel pieces. The burst of off-gas at the early in the dissolution of fuel powder seems to be avoidable with setting the appropriate dissolution condition, and it is important to optimize the dissolution condition with considering the capacity of off-gas treatment process.
JNC TN8400 2000-030, 17 Pages, 2000/12
As a representative of natural marine groundwater, the author selected pumped water from a Quaternary sedimentary aquifer of the Mobara gas-field in Japan and measured the concentration of total organic carbon (TOC) and of organic acid anions (formic, acetic, lactic, succinic, humic, fulvic, propionic, valeric and butyric acids). The concentration of TOC ranged from 22 1 to 24
1 to 24 0mg/L. As organic acid anions, only succinic and fulvic acids were detected and each concentration was given to be from 5.8
0mg/L. As organic acid anions, only succinic and fulvic acids were detected and each concentration was given to be from 5.8 0.5 to 8.3
0.5 to 8.3 0.3 and from 3.3
0.3 and from 3.3 0.2 to 3.5
0.2 to 3.5 0.2mg/L, respectively. By consideration of the temperature and the [SO
0.2mg/L, respectively. By consideration of the temperature and the [SO
 ] of the groundwater, it is inferred that the organic acid has been significantly decomposed by activities of microbes, such as the fermentation process, CH
] of the groundwater, it is inferred that the organic acid has been significantly decomposed by activities of microbes, such as the fermentation process, CH COO
COO + H
+ H O = HCO
O = HCO
 + CH
+ CH .
.
Yamanaka, Shinsuke*; Abe, Kazuyuki
JNC TY9400 2000-004, 78 Pages, 2000/03
no abstracts in English
 gas cooled reactor
gas cooled reactor; ; Mizuta, Shunji
JNC TN9400 2000-040, 41 Pages, 2000/03
The corrosion behavior of ferritic stainless steels applied to core components under C0 gas environment was investigated in order to be helpful to fuel design in C0
gas environment was investigated in order to be helpful to fuel design in C0 gas cooled reactor as the feasibility study for fast breeder reactor. The dependence of the corrosion behavior, before a breakaway occurs, on C0
gas cooled reactor as the feasibility study for fast breeder reactor. The dependence of the corrosion behavior, before a breakaway occurs, on C0 gas temperature, Si and Cr contents of ferritic steels was determined quantitatively. The following correlations to calculate the metal loss thickness was established. X = 4.4w w = √(k
gas temperature, Si and Cr contents of ferritic steels was determined quantitatively. The following correlations to calculate the metal loss thickness was established. X = 4.4w w = √(k t) k =
t) k = 
 exp( - 5.45[Si])
exp( - 5.45[Si])  exp( - 1.09[Cr])
exp( - 1.09[Cr])  exp( - 11253/T)
exp( - 11253/T)  = 1.65
= 1.65  10
10
 4.40
4.40  10
10 X : metal loss thickness[
X : metal loss thickness[ ml, w : corrosion weight gain [mg/cm
ml, w : corrosion weight gain [mg/cm ] k : parabola constant [(mg/cm
] k : parabola constant [(mg/cm )
) /hr], t : time [hr],
/hr], t : time [hr],  : constant [Si] : Si content[wt.%], [Cr] : Cr content [wt.%], T : temperature [K]
: constant [Si] : Si content[wt.%], [Cr] : Cr content [wt.%], T : temperature [K]
Nagasaki, Shinya*
JNC TJ8400 2000-004, 32 Pages, 2000/02
Equilibrium and kinetics of sorption of NpO on illite were investigated at pH = 6 by using the differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry method and the spectroscopic method, respectively. It was found that the sorption isotherm obtained was fitted better by the Langmuir-Freundlich type equation than by the Langmuir equation. The heterogeneity coefficient was 0.89
on illite were investigated at pH = 6 by using the differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry method and the spectroscopic method, respectively. It was found that the sorption isotherm obtained was fitted better by the Langmuir-Freundlich type equation than by the Langmuir equation. The heterogeneity coefficient was 0.89  0.05 and the half width at half maximum (HWHM) of affinity spectrum was 0.19 log unit, indicating that the surfacc of illite used has a low degree of heterogeneity. The kinetic spectra indicated that the sorption of NpO
0.05 and the half width at half maximum (HWHM) of affinity spectrum was 0.19 log unit, indicating that the surfacc of illite used has a low degree of heterogeneity. The kinetic spectra indicated that the sorption of NpO occurs only at the outer surfacc. The mean HWHM of the kinetic spectra was 0.18 log unit. This also proves that the sorption kinetics of NpO
occurs only at the outer surfacc. The mean HWHM of the kinetic spectra was 0.18 log unit. This also proves that the sorption kinetics of NpO on the illite used is controlled by the same heterogeneity of the sorption sites. From the dependence of mean rate constants on temperature, a mean apparent activation enthalpy and a mean apparent activation entropy were evaluated at 37
on the illite used is controlled by the same heterogeneity of the sorption sites. From the dependence of mean rate constants on temperature, a mean apparent activation enthalpy and a mean apparent activation entropy were evaluated at 37 3 kJ/mol and - 69
3 kJ/mol and - 69  7 J/K
7 J/K mol, respectively. This value of enthalpy suggests that the sorption is not controlled by diffusion through the hydrodynamic film around the illite. Equilibrium and kinetics of sorption of NpO
mol, respectively. This value of enthalpy suggests that the sorption is not controlled by diffusion through the hydrodynamic film around the illite. Equilibrium and kinetics of sorption of NpO and Np(V) carbonate complexes (mainly NpO
and Np(V) carbonate complexes (mainly NpO CO
CO ) on Na-montmorillonite were also examined by using same technique.
) on Na-montmorillonite were also examined by using same technique.
Mizuta, Shunji; ;
JNC TN9400 99-082, 60 Pages, 1999/10
The density measurement of the internal creep specimens irradiated in FFTF/MOTA (Fast Flux Test Facility / Material open Test Assembly) was conducted MMF (Materia1 Monitoring Facility) and accurate separation of swelling strain from total strain leaded in the derivation of the irradiation creep coefficients. Irradiation creep coefficients for PNC 316, 15Cr-20Ni base S.S. and 14Cr-25Ni base S.S. were systematically expressed, while thermal creep coefficients K, under irradiation were separately expressed for above three steels. The results obtained are follows, (1)The effect of stress induced swelling was recognized in the temperature range from 405 to 605 C. The swelling in high stress specimens have a tendency to increasing swelling. (2)The irradiation creep coefficients derived from PNC316 and l5Cr-20Ni are similar to that of derived from 20%CW316S.S., CW316Ti and CW15-15Ti which were reported by other authors. (3)The irradiation creep coefficient derived from gas pressurized tube irradiation using FFTF/MOTA expressed appropriately irradiation creep strain from fuel pins using FFTF/MFA-2(15Cr-2ONi base S.S.).
C. The swelling in high stress specimens have a tendency to increasing swelling. (2)The irradiation creep coefficients derived from PNC316 and l5Cr-20Ni are similar to that of derived from 20%CW316S.S., CW316Ti and CW15-15Ti which were reported by other authors. (3)The irradiation creep coefficient derived from gas pressurized tube irradiation using FFTF/MOTA expressed appropriately irradiation creep strain from fuel pins using FFTF/MFA-2(15Cr-2ONi base S.S.).
 C-carbon fiber composite irradiated with low energy deuterium ions
C-carbon fiber composite irradiated with low energy deuterium ionsJimbo, Ryutaro*; Nakamura, Kazuyuki; Bandourko, V.*; Dairaku, Masayuki; Okumura, Yoshikazu; Akiba, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 266-269, p.1103 - 1107, 1999/00
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:40.64(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
;
JNC TN9400 98-005, 40 Pages, 1998/11
Thermal conductivity of uranium-plutonium mixed oxide fuel for fast reactor at beginning-of-life was re-correlated in order to apply to the fuel design and the fuel pin performance analysis. Thermal conductivity of actual fuel with porosity ( ), that of fully dense fuel (
), that of fully dense fuel (
 ) and porosity correction factor (F) has theoretically the following correlation :
) and porosity correction factor (F) has theoretically the following correlation :  = F
= F
 , The database (221 points) were selected by adopting following criteria: "validated by different authors and methods" and "high density fuel specimens around 95% of theoretical density". The database were corrected to fully dense condition by modified Loeb equation : F=1-2.5P (P: fractional porosity) and then correlated by the least square method program. The electron conduction term of uranium dioxide reported by Harding was used in order to compensate for the lack of the high temperature range data. New correlation for fully dense fuel was developed again and shown below, which the data base used in the analysis ranged from 20 to 30% for plutonium content in heavy metal atoms, 1.98 and 2.00 for oxygen to metal ratio, from 94.3 to 96.4% of theoretical density and from 64 to 2279
, The database (221 points) were selected by adopting following criteria: "validated by different authors and methods" and "high density fuel specimens around 95% of theoretical density". The database were corrected to fully dense condition by modified Loeb equation : F=1-2.5P (P: fractional porosity) and then correlated by the least square method program. The electron conduction term of uranium dioxide reported by Harding was used in order to compensate for the lack of the high temperature range data. New correlation for fully dense fuel was developed again and shown below, which the data base used in the analysis ranged from 20 to 30% for plutonium content in heavy metal atoms, 1.98 and 2.00 for oxygen to metal ratio, from 94.3 to 96.4% of theoretical density and from 64 to 2279 C for temperature.
C for temperature. 
 =
= 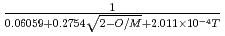 +
+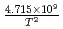 exp(
exp(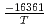 ) where...
) where...
 : Thermal conductivity of fully dense MOX fuel for fast reactor (W/mK). T: Temperature (K). O/M: Oxygen-to-metal ratio (-). The above correlation could be applied for fully dense and typical MOX fuel pellet of fast reactor ranging from room temperature up to melting point.
: Thermal conductivity of fully dense MOX fuel for fast reactor (W/mK). T: Temperature (K). O/M: Oxygen-to-metal ratio (-). The above correlation could be applied for fully dense and typical MOX fuel pellet of fast reactor ranging from room temperature up to melting point.
C.L.Wang*; Hirade, Tetsuya; Maurer, F. H. J.*; Eldrup, M.*; N.J.Pedersen*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 108(11), p.4654 - 4661, 1998/03
Times Cited Count:153 Percentile:97.11(Chemistry, Physical)no abstracts in English
; Kano, Shigeki; ; Tachi, Yoshiaki; Hirakawa, Yasushi; Yoshida, Eiichi
PNC TN9410 98-021, 68 Pages, 1998/02
Engineering ceramics have excellent properties such as high strength, high hardness and high heat resistance compared with metallic matelials. To apply the ceramic in fast reactor environment, it is necessary to evaluate the sodium compatibility and the influence of sodium on the mechanical properties of ceramics. In this study, the influence of high temperature sodium on the mechanical properties of sintered ceramics of conventional and high purity Al O
O , SiC, SiAlON, AlN and unidirectional solidified ceramics of Al
, SiC, SiAlON, AlN and unidirectional solidified ceramics of Al O
O /YAG eutectic composite were investigated by means of flexure tests. Test specimens were exposed in liquid sodium at 823K and 923K for 3.6Ms. There were no changes in the flexural strength of the conventional and high purity Al
/YAG eutectic composite were investigated by means of flexure tests. Test specimens were exposed in liquid sodium at 823K and 923K for 3.6Ms. There were no changes in the flexural strength of the conventional and high purity Al O
O , AlN and Al
, AlN and Al O
O /YAG eutectic composite after the sodium exposure at 823K. On the contrary, the decrease in the flexural strength was observed in SiC and SiAlON. After the sodium exposure at 923K, there were also no changes in the flexural strength of AlN and Al
/YAG eutectic composite after the sodium exposure at 823K. On the contrary, the decrease in the flexural strength was observed in SiC and SiAlON. After the sodium exposure at 923K, there were also no changes in the flexural strength of AlN and Al O
O /YAG eutectic composite. In the conventional and high purity Al
/YAG eutectic composite. In the conventional and high purity Al O
O and SiC, the flexural strength decreased and signs of grain boundary corrosion were detected by surface observation. The flexural strength of SiAlON after the sodium exposure at 923K increased instead of severe corrosion. In the specimens those showed no changes in the flexural strength, further exposure in sodium is needed to verify whether the mechanical properties degrade or not. For SiAlON, it is necessary to clarify the reason for the increased strength after the sodium exposure at 923K.
and SiC, the flexural strength decreased and signs of grain boundary corrosion were detected by surface observation. The flexural strength of SiAlON after the sodium exposure at 923K increased instead of severe corrosion. In the specimens those showed no changes in the flexural strength, further exposure in sodium is needed to verify whether the mechanical properties degrade or not. For SiAlON, it is necessary to clarify the reason for the increased strength after the sodium exposure at 923K.
Jimbo, Ryutaro*; Nakamura, Kazuyuki; Bandourko, V.*; Okumura, Yoshikazu; Akiba, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 258-263, p.724 - 728, 1998/00
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:57.28(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)no abstracts in English
; ;
PNC TN9410 98-014, 46 Pages, 1997/11
Thermal conductivity of uranium-plutonium mixed oxide fuel for fast reactor at beginning-of-life was correlated based on the recent results in order to apply to the fuel design and the fuel performance analysis. A number of experimental results of unirradiated fuel speimens were corrected from open literatures and PNC internal reports and examined for the database. Thermal conductivity of acutual fuel with porosity ( ), that of fully dense fuel (
), that of fully dense fuel ( 100%TD) and porosity correction factor (F) had theoretically the following correlation :
100%TD) and porosity correction factor (F) had theoretically the following correlation :  = F
= F 100%TD. The following correlation was developed for fully dense fuel by the results of high density fuel pellets which the effect of porosity was relatively small. The data base ranged from 17 to 30% for plutonium content in heavy metal atoms, from 1.90 to 2.00 for oxygen to metal ratio, from 90 to 98% of theoretical density and from 400 to 2090 degree C for temperature.
100%TD. The following correlation was developed for fully dense fuel by the results of high density fuel pellets which the effect of porosity was relatively small. The data base ranged from 17 to 30% for plutonium content in heavy metal atoms, from 1.90 to 2.00 for oxygen to metal ratio, from 90 to 98% of theoretical density and from 400 to 2090 degree C for temperature. 
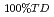 = (1/(-0.03237+0.8606
= (1/(-0.03237+0.8606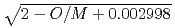 +2.483
+2.483 10
10 T))+75.27
T))+75.27 10
10 T
T where
where  100%TD: Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) T: Temperature (K) O/Z: Oxygen-to-metal ratio (-) In this work two porosity correction factors were needed for high density fuel and low density fuel (around the current Monju specification). For high density fuel (as-fabricated fuel density :
100%TD: Thermal Conductivity (W/mK) T: Temperature (K) O/Z: Oxygen-to-metal ratio (-) In this work two porosity correction factors were needed for high density fuel and low density fuel (around the current Monju specification). For high density fuel (as-fabricated fuel density :  90%TD) F
90%TD) F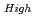 = 1-2.95P(P:Porosity volume Fraction (-)) For low density fuel (as-fabricated fuel density: around 85%TD) F
= 1-2.95P(P:Porosity volume Fraction (-)) For low density fuel (as-fabricated fuel density: around 85%TD) F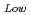 = 1-1.4P (P: Porosity volume Fraction (-)) The universal porosity correction factor was not determined in this work. In the next step, theoretical and analytical considerations should be taken into account.
= 1-1.4P (P: Porosity volume Fraction (-)) The universal porosity correction factor was not determined in this work. In the next step, theoretical and analytical considerations should be taken into account.